
Note
This documentation is for a development version of IPython. There may be significant differences from the latest stable release (1.2.1).
April, 2014
IPython 2.0 requires Python ≥ 2.7.2 or ≥ 3.2.1. It does not support Python 3.0, 3.1, 2.5, or 2.6.
The principal milestones of 2.0 are:
Contribution summary since IPython 1.0 in August, 2013:
The amount of work included in this release is so large that we can only cover here the main highlights; please see our detailed release statistics for links to every issue and pull request closed on GitHub as well as a full list of individual contributors.
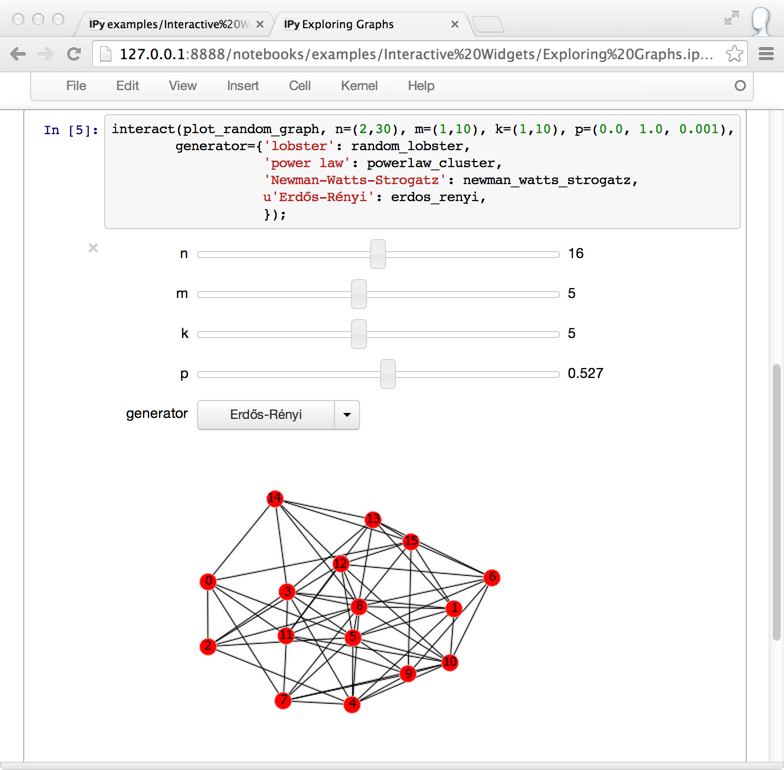
Available in the new IPython.html.widgets module, widgets provide an easy way for IPython notebook users to display GUI controls in the IPython notebook. IPython comes with bundle of built-in widgets and also the ability for users to define their own widgets. A widget is displayed in the front-end using using a view. For example, a FloatRangeWidget can be displayed using a FloatSliderView (which is the default if no view is specified when displaying the widget). IPython also comes with a bundle of views and the ability for the user to define custom views. One widget can be displayed multiple times, in on or more cells, using one or more views. All views will automatically remain in sync with the widget which is accessible in the back-end.
The widget layer provides an MVC-like architecture on top of the comm layer. It’s useful for widgets that can be expressed via a list of properties. Widgets work by synchronizing IPython traitlet models in the back-end with backbone models in the front-end. The widget layer automatically handles
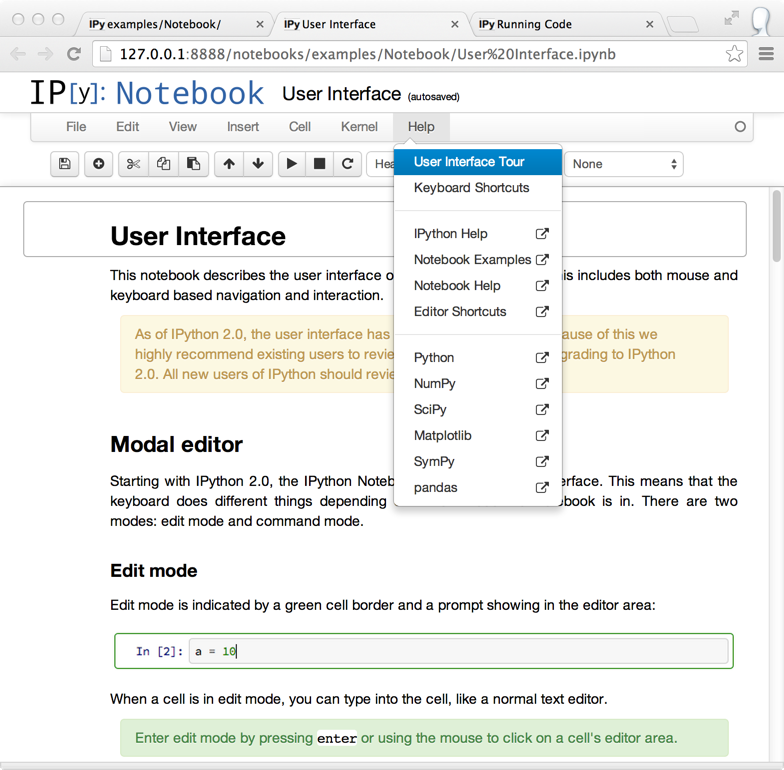
Familiarize yourself with the updated notebook user interface, including an explanation of Edit and Command modes, by going through the short guided tour which can be started from the Help menu.
To prevent untrusted code from executing on users’ behalf when notebooks open, we have added a signature to the notebook, stored in metadata.
For more information, see Signing Notebooks.
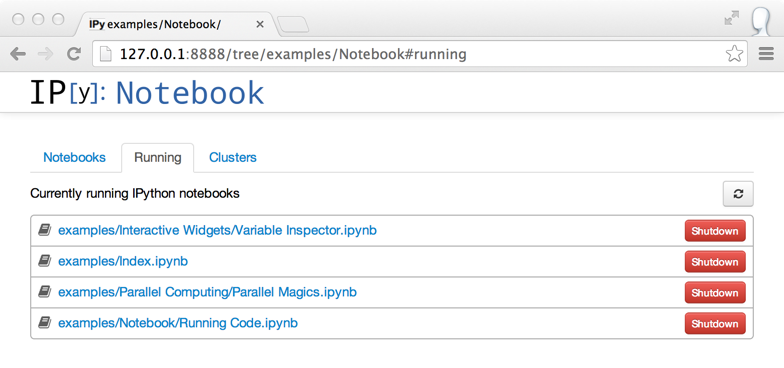
The dashboard now has a “Running” tab which shows all of the running notebooks.
IPython previously supported Python 3 by running 2to3 during setup. We have now switched to a single codebase which runs natively on Python 2.7 and 3.3.
For notes on how to maintain this, see Writing code for Python 2 and 3.
Some configurable traits are containers (list, dict, set) Config objects now support calling extend, update, insert, etc. on traits in config files, which will ultimately result in calling those methods on the original object.
The effect being that you can now add to containers without having to copy/paste the initial value:
c = get_config()
c.InlineBackend.rc.update({ 'figure.figsize' : (6, 4) })
adds use_dill() for allowing dill to extend serialization support in IPython.parallel (closures, etc.). Also adds DirectView.use_dill() convenience method for enabling dill locally and on all engines with one call.
The IPython console lexer has been rewritten and now supports tracebacks and customized input/output prompts. See the new lexer docs for details.
There was no official way to query or remove callbacks in the Formatter API. To remedy this, the following methods are added to BaseFormatter:
All of the above methods raise a KeyError if no match is found.
And the following methods are changed:
Formatters can now raise NotImplementedError in addition to returning None to indicate that they cannot format a given object.
Exceptions are no longer silenced when formatters fail. Instead, these are turned into FormatterWarnings. A FormatterWarning will also be issued if a formatter returns data of an invalid type (e.g. an integer for ‘image/png’).
Python 2.6 and 3.2 are no longer supported: the minimum required Python versions are now 2.7 and 3.3.
The Transformer classes have been renamed to Preprocessor in nbconvert and their call methods for them have been renamed to preprocess.
The call methods of nbconvert post-processsors have been renamed to postprocess.
The module IPython.core.fakemodule has been removed.
The alias system has been reimplemented to use magic functions. There should be little visible difference while automagics are enabled, as they are by default, but parts of the AliasManager API have been removed.
We fixed an issue with switching between matplotlib inline and GUI backends, but the fix requires matplotlib 1.1 or newer. So from now on, we consider matplotlib 1.1 to be the minimally supported version for IPython. Older versions for the most part will work, but we make no guarantees about it.
The pycolor command has been removed. We recommend the much more capable pygmentize command from the Pygments project. If you need to keep the exact output of pycolor, you can still use python -m IPython.utils.PyColorize foo.py.
IPython.lib.irunner and its command-line entry point have been removed. It had fallen out of use long ago.
The input_prefilter hook has been removed, as it was never actually used by the code. The input transformer system offers much more powerful APIs to work with input code. See Custom input transformation for details.
IPython.core.inputsplitter.IPythonInputSplitter no longer has a method source_raw_reset(), but gains raw_reset() instead. Use of source_raw_reset can be replaced with:
raw = isp.source_raw
transformed = isp.source_reset()
The Azure notebook manager was removed as it was no longer compatible with the notebook storage scheme